Every Winter this comes up. As a Realtor and property manager, I’ve had plenty of firsthand experience here. I think the best way to categorize this article is to break it into two parts; prevention during construction, and repair measures to address ice dams that form after construction. First, let’s go over what an ice dam is, and why it occurs.
Ice damming, what is it, and why does it occur?
Most homes have a roof overhang that extends behind the house. The area that extends beyond the house is not heated whereas the area directly above the living area of the home will inevitably realize some heat loss. As that heat rises into the attic space above the ceiling and insulation, it ultimately reaches the bottom side of the roof which will begin to melt the snow on the roof. The water then begins to travel down the roof. As it reaches the unheated portion of the roof overhang, it re-freezes. This is where an ice dam is formed. The longer this occurs, the further the ice backs up towards the heated portion of the roof, possibly finding an entry point for water into the living areas of the home.
New Construction
It’s impossible to predict where or how an ice dam is going to form. However, we can take some preventive steps, and it’s best to pay special attention to the North side of your project where the roof will see the least amount of sun to help melt away snow and ice. The first line of defense is going to be proper soffit and roof ventilation. If you can prevent the residual heat from warming the underside of the roof and melting snow, we can minimize the amount of ice that will form it on the unheated areas of the roof. This can be done a few different ways.
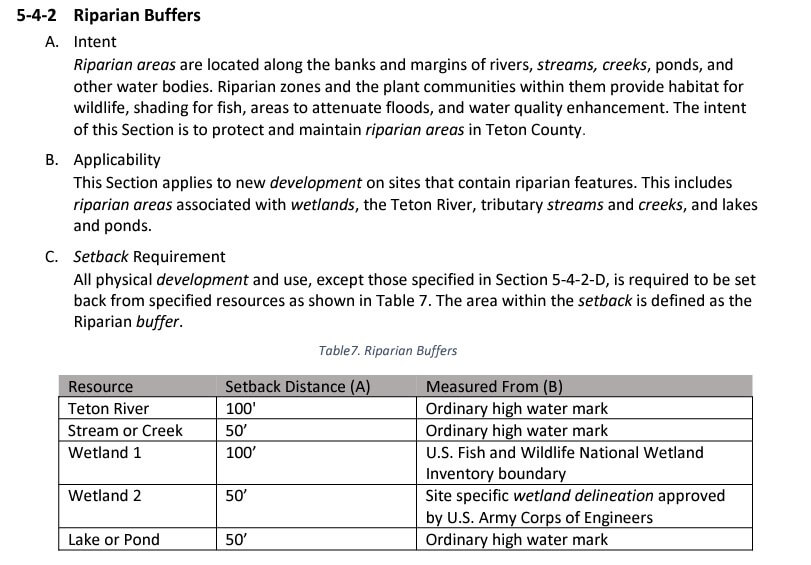
Ventilation
Usually a proper roof ventilation system will include soffit vents on the underside of the unheated roof overhang portion of the roof as well as roof vents near the top or highest point of the roof where rising heat can escape. Normally your insulator will install what are called “baffles” which prevent the insulation that will be later added from covering the vents in the soffit or roof overhang. It is absolutely key that you have this section inspected before and after insulation (if possible) to ensure that the baffles are not crushed or moved during the insulation process, thus covering the vents and not allowing airflow. I have also seen additional venting in gable ends and even power vent fans to help push the warm air out of the attic cavity. Understanding that not all roof designs have an attic, it doesn’t necessarily mean that the roof cannot be ventilated. I have built shed roof style homes and installed plywood to create a small gap the full length of the roof from the bottom end all the way up to the ridge to add a layer of air ventilation just as a precautionary measure, even on a roof that would normally slide snow such as a metal roof.
Insulation
Insulation is one of those sensitive topics with me. I have my own opinions on insulation types and where they are best applied, but I’ll save that for another article. If you do have a home design with an attic, it’s more affordable than you might think to add more insulation than the building code requires. If we can slow down the heat loss into the attic, we can slow down how much snow begins to melt on the underside of the roof. While the code does require substantial insulation in roofs in our area, there’s good reason to consider overdoing it if you’re going to upgrade something.
Ice and water shield
Most builders will install a waterproof membrane from the roof’s edge beyond the habitable space in the house. As the water backs up, it will be stopped by this impermeable layer, or at least that’s the idea. With every construction job that I’ve been involved with, I’ve opted for ice and water shield on the entire surface of the roof. Yes, this is an added cost. However, ice dams aren’t the only things that cause leaks and the extra insurance might be something to consider.
Existing Construction
The more time you spend in Teton Valley the more you will realize that not every winter is the same. One season might not create any ice damming issues while the next creates significant problems. It’s all about freeze/thaw, temperature, sun, snow load, the list goes on. That being said, almost everybody is going to experience an ice damming problem if they form a long-term relationship with Teton Valley. If you do, I think it’s important to look at causation and repair options.
What is causing the ice dam?
We can go back to the new construction measures to see if they were properly applied with the existing construction. Usually attic spaces are accessible (even though it isn’t very much fun) and those insulation baffles, assuming they exist, can sometimes be inspected after the fact. If one finds that there is no attic ventilation or poor ventilation, roof vents or gable vents can be added after the fact relatively easily. It’s a great time to assess the damage in the Winter months, and be prepared to make repairs in the Summer months when it is safer to do so.
Remedy Option 1, Vents
As mentioned above, roof vents can be installed after the fact. This can be great option to help expel some of the heat out of the attic space. In extreme cases where ventilating the existing roof is impossible, there have been projects (even locally) that have built a replacement roof on top of the existing roof that is ventilated to provide that much needed air gap.
Remedy Option 2, Heat cable
Sometimes heat cable is a necessary evil. We tend to avoid it or turn it off because of the cost, but if it saves us from expensive damages inside our home, it may be the only option available. Heat tape comes in many forms from budget DIY to professionally engineered and installed systems. Further, these systems can be installed with a simple electrical outlet, or hardwired into a 220 volt breaker. The severity of the issue is usually an indicator as to which direction might be best. Either way, remember to extend the heat cable beyond the unheated portion of the roof to above the heated portion for the most effective results.
Remedy Option 3, Shoveling and/or Steaming
Roof shoveling (be sure to consider someone who is insured) can be an easy and effective remedy, especially when an issue is discovered mid-season. In addition, roof steaming is an effective option to remove stubborn ice dams without damaging your roof, but it’s usually an expensive one.
Obviously I am a Realtor, not a builder. Check with your contractor on these ideas, and be careful!