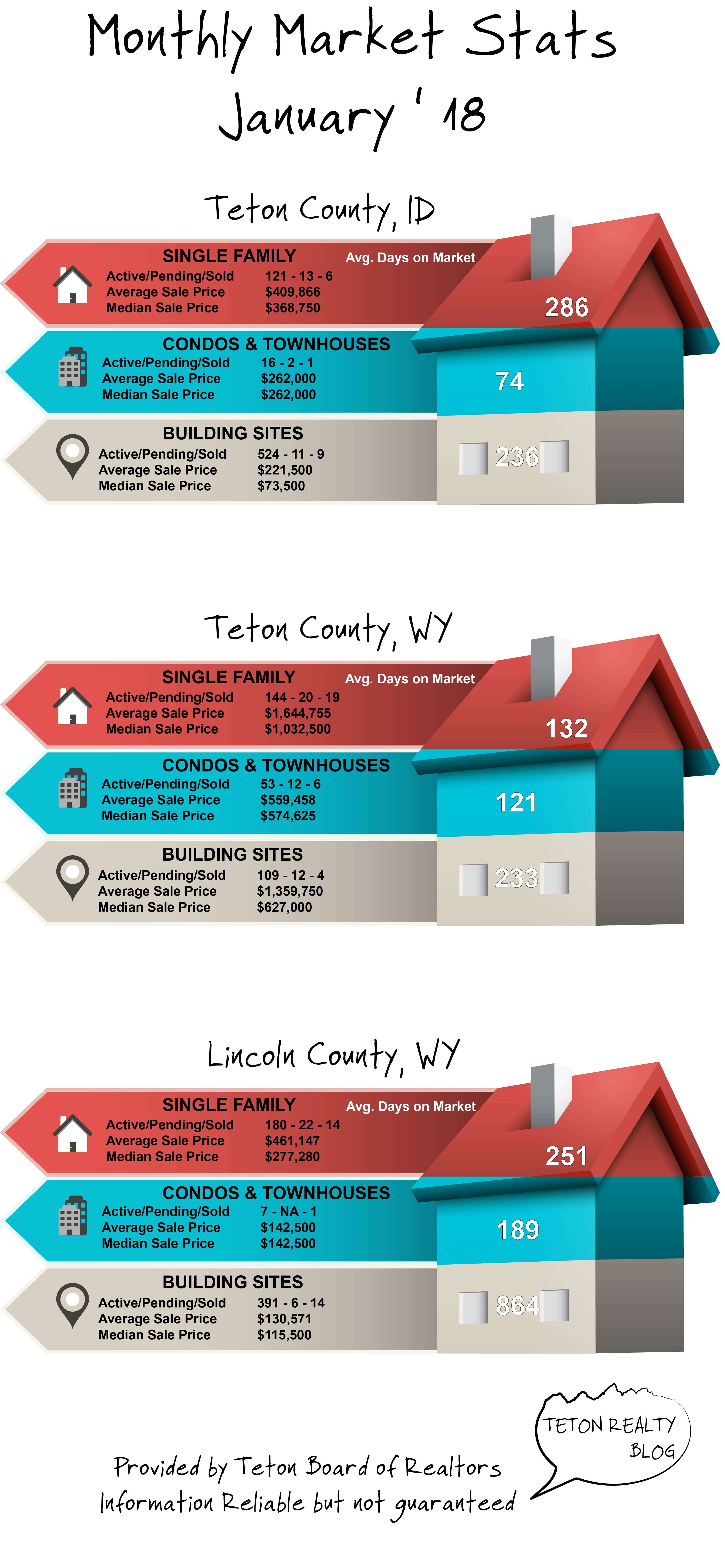
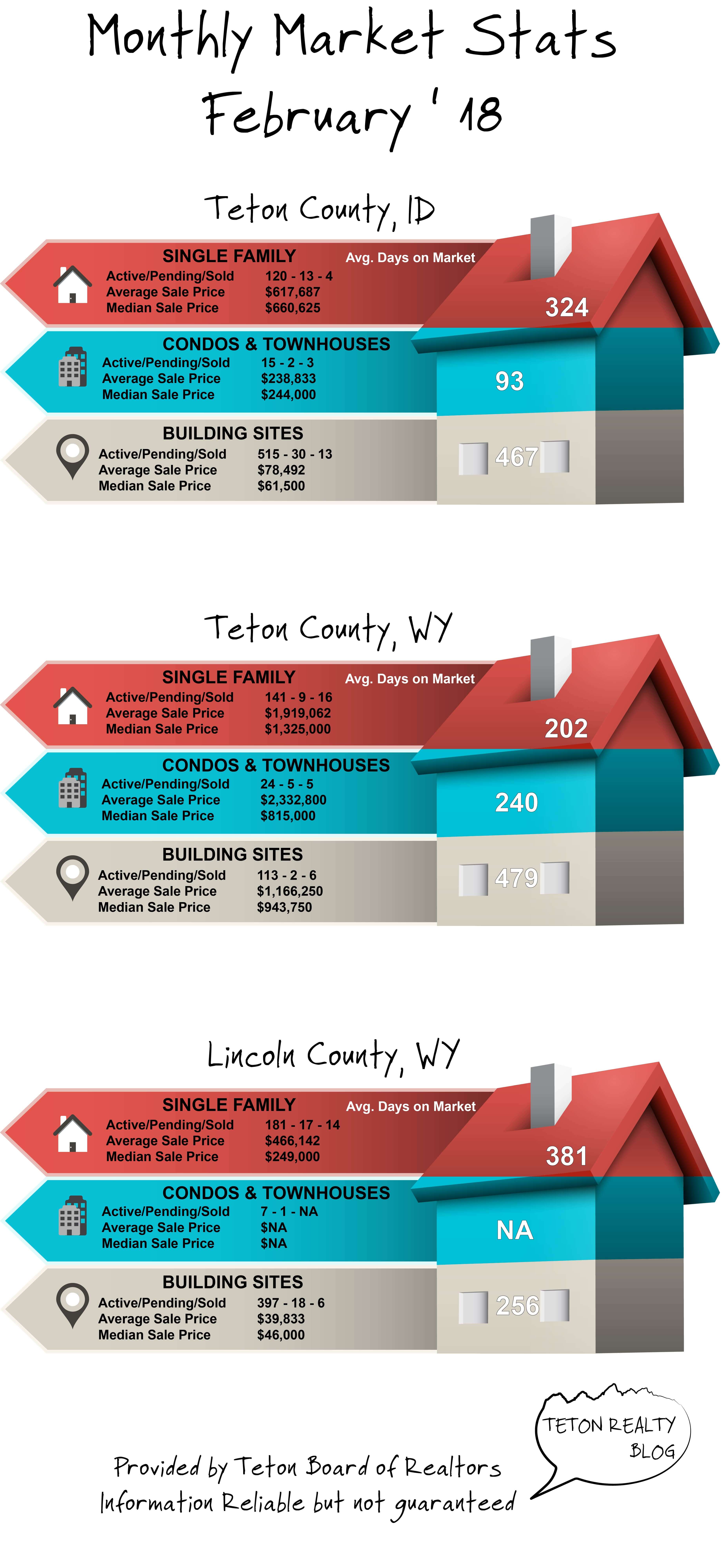
March ’18 Market Stats

Teton Region Real Estate Market Stats, Articles & News

 While it may not seem like a big topic to someone in the community not involved with real estate, fire suppression compliance, (or the lack thereof) has recently been a big topic for those in the real estate community.
While it may not seem like a big topic to someone in the community not involved with real estate, fire suppression compliance, (or the lack thereof) has recently been a big topic for those in the real estate community.-Grant Durtstchi – 208-705-7200
-AW Engineering – 208-787-2952
-Wilder System Solutions – 208-456-2287